Written by

06th February 2020 – Written by Sanjay M Parekh, PhD – At RSNA 2019, there was a record number of AI vendors exhibiting at the conference, prompting the organisers to host the AI Showcase in a designated hall adjacent from the two main halls. The consensus from vendors exhibiting in the AI Showcase was mixed. Some vendors reported a reduced footfall, but other vendors reported more productive discussions with potential buyers that visited their booths. Although the dedicated AI Showcase has become a necessity, it may have inadvertently positioned AI as a sideshow, rather than an integral part of the main conference.
Throughout the conference, there were several prominent trends for AI in radiology and it was clear that the industry is making strides in addressing the barriers for mass-market adoption. Below, we describe three trends that are expected to have a significant impact on the market over the next few years.
Medical Imaging AI Platforms (Workflow Integration)
The ‘last mile’ challenge faced by AI vendors is the successful deployment and integration of AI algorithms into clinical workflows. To address this challenge, some vendors (typically PACS vendors) have released dedicated medical imaging AI platforms that integrate AI into clinical practice.
These medical imaging AI platforms perform various tasks, including (1) routing of scans to the appropriate AI application; (2) AI inferencing; (3) displaying the AI results in the diagnostic viewer; (4) enabling the radiologist to edit, accept or reject the AI results, all from a single user interface; and (5) sending the final AI results to the PACS to be integrated back into the worklist.
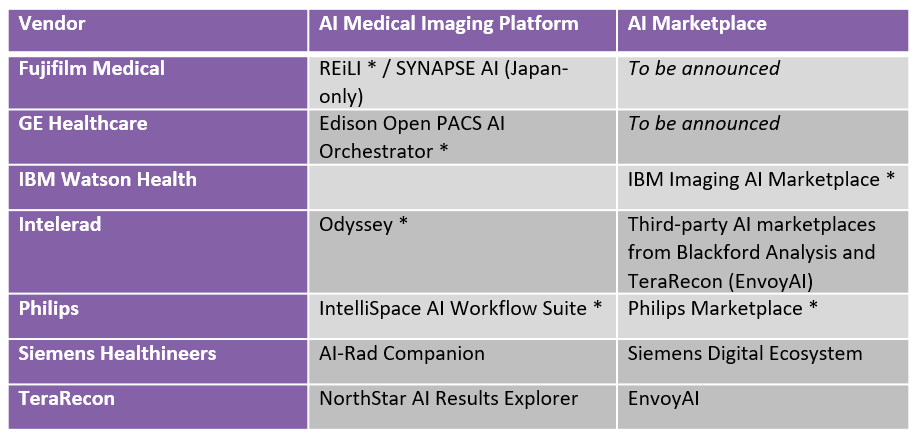
Vendors with dedicated AI platforms include GE Healthcare (Edison Open PACS AI Orchestrator), Siemens Healthineers (AI-Rad Companion) and Philips (IntelliSpace AI Workflow Suite). GE Healthcare and Siemens Healthineers are partnering with third-party developers and concurrently developing native AI algorithms, while Philips is mainly focused on partnerships.
Vendors are typically bundling AI marketplaces with their AI platforms, providing radiologists with a means to select and purchase algorithms from a range of third-party developers. The following table details the medical imaging AI platforms and the AI marketplace offerings from some of the PACS vendors.
*announced at RSNA
Other PACS vendors, including Sectra, Agfa HealthCare, and Change Healthcare, have chosen to integrate AI capabilities and algorithms directly into their core imaging IT platforms through custom integrations. Arterys has a native web-based platform with a browser-based user interface and at RSNA 2019 it announced Arterys Marketplace, with both native and third-party algorithms.
Medical imaging AI platforms are seen as a solution for the deployment and orchestration of AI algorithms in the clinical workflow and the integration of AI results in the diagnostic viewer environment. These dedicated platforms will facilitate the scaling of AI in radiology.
Image Reconstruction
The second trend we observed at RSNA 2019 is image reconstruction solutions using deep learning, especially for CT and MR imaging. AlgoMedica (PixelShine) is using deep learning to improve the quality of low-dose CT scans to that of normal-dose CT scans, significantly reducing the patient’s exposure to radiation. This is especially important for patients requiring multiple, or regular, follow-up scans.
For MR imaging, Subtle Medical (SubleMR) is using deep learning to reduce the scan time, whilst ensuring image resolution is maintained. Previous techniques have led to iterative reductions in scan time but using deep learning, Subtle Medical hopes to achieve a step-change in reducing scan times whilst maintaining a high signal to noise ratio and image resolution. This will be beneficial for paediatric, claustrophobic or seriously ill patients, some of whom have difficulties remaining still for long periods.
Canon Medical announced the roll-out of Advanced intelligent Clear-IQ Engine (AiCE) directly onto its new CT and MR scanners, enabled by edge computing. AiCE improves image acquisition for CT scans (by lowering the dose) and MR scans (by shortening the scan duration) using deep learning algorithms at the point-of-scan rather than the point-of-read (for example on the PACS).
It is expected that deep learning-based image reconstruction technologies will improve the patient experience, in terms of reduced time in the scanner, lower contrast dose, and faster appointments. These technologies will also provide a measurable return-on-investment for the healthcare provider by scanning more patients in a day and reducing the number of re-scans (typically due to artefact formation or poor image quality). Additionally, they will enable point-of-care CT and MR imaging. For example, Hyperfine’s portable MRI scanner, which pending US-FDA 510(k) approval is expected to sell for approximately $50,000.

Non-Invasive Biomarkers
One of the more established trends we saw at RSNA 2019 was AI solutions for quantifying non-invasive imaging biomarkers. These solutions automate and speed up the time-consuming process of manually taking measurements, and the results are more accurate and reproducible. Non-invasive biomarkers support clinicians in treatment planning decisions, for example when measuring a patient’s response to receiving a new drug and may reduce the need for invasive procedures such as biopsy.
Neurology is the clinical area where there has been significant progress in developing non-invasive biomarkers. CorTechs Labs provides volumetric measurements of brain structures compared to a normative database adjusted for age, sex, and intracranial volume. icometrix extracts clinically relevant biomarkers from MR imaging scans of patients with neurological disorders or traumatic brain injury.
Moving forward, we expect the development of non-invasive biomarkers for liver and prostate, followed by other body areas, such as musculoskeletal. QUIBIM offers its Precision platform, which provides quantitative imaging biomarkers for the liver, as well as the prostate and musculoskeletal system. Perspectum Diagnostics showcased its LiverMultiScan solution, which characterises liver tissue, identifying patients susceptible to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and those eligible for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) drugs, which are due to be commercialised in 2020. Median Technology has an image-based phenotype platform (iBiopsy), which provides fully automated imaging liver biomarkers to inform clinical decisions, based on patient-profiling from real-world evidence. HealthLytix is one of the first vendors to receive US FDA clearance for its RSI-MRI+ solution, which increases the visibility of imaging biomarkers of cancerous tissue in the prostate.
We observed several other AI-related trends at RSNA 2019, including AI marketplaces for radiology, body area solutions, complete workflow solutions (end-to-end application of AI to a particular use case), computer-aided triage, edge AI (deployment of AI solutions on the scanner itself), predictive analytics (predicting patient’s risk of developing disease using imaging data), and portfolio diversification (development a collection of diverse AI algorithms to address a broad range of conditions).
We have written a more in-depth analysis for each of these trends in our RSNA 2019 Post-Show report, which is available for purchase. For more information, or to discuss trends in greater detail, please contact the author: Sanjay M Parekh, PhD (Sanjay.Parekh@SignifyResearch.net).
About Signify Research
Signify Research is an independent supplier of market intelligence and consultancy to the global healthcare technology industry. Our major coverage areas are Healthcare IT, Medical Imaging and Digital Health. Our clients include technology vendors, healthcare providers and payers, management consultants and investors. Signify Research is headquartered in Cranfield, UK.